11 mins read
What is CSI MasterFormat? Defining the Standard for Construction Specification Organization

Developing standard practices and codes for an industry as complex and diverse as construction is a lofty ambition. Still, the Construction Specifications Institute in North America has successfully accomplished this with its versatile MasterFormat system. This ingenious method allows project teams to distill the endless variety of work items and specifications through a logical “filing system.”
In this blog post, we review the history, purpose, and structure of CSI MasterFormat to better understand how it became a common language for many construction industry professionals.
What Is CSI MasterFormat?
CSI MasterFormat is a numerical system developed by the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) to organize and communicate project information. The hierarchical system consists of 50 divisions representing specific areas of construction work.
MasterFormat is widely regarded as the industry standard, mainly in North America. Over 60 years of updates and optimization have been completed since the method was initially launched in 1963 as the “Master Specification System,” with just 16 major divisions.
The first official version under the MasterFormat name was launched in 1978 as a joint effort between CSI and Construction Specifications Canada (CSC). In 2004, the format was expanded to 50 divisions to accommodate new categories like facilities management, telecommunications, and computer technology, as well as any future divisions that might be deemed necessary.
As construction software solutions and new technologies like building information modeling (BIM) gain acceptance, the MasterFormat divisions and categories established decades ago continue to serve a valuable purpose in the digital age.
Who Benefits from MasterFormat?
Specifiers, engineers, and architects are the most obvious beneficiaries of a system equipped to organize and communicate construction specifications throughout all project phases. The system also ensures consistency and clarity in released documentation. MasterFormat simplifies tasks for many other disciplines, including:
- Designers and preconstruction teams enjoy easy information access
- Contractors, project managers, and facility managers are coordinating tasks
- Product manufacturers seeking a common language to specify items
Construction estimators also enjoy the benefits of MasterFormat, as they use the logical divisions to organize estimates and ensure no important items are missed. The same benefit applies to contractors who roll up estimates from multiple subcontractors into their overall bids and estimates.
What Is the Purpose of the CSI MasterFormat?
CSI MasterFormat was created when the industry was overwhelmed by the variety and inconsistency of specification organization between companies, projects, and individual contributors. The original purpose of ensuring consistent communication and organization is still applicable, but the MasterFormat standard also has additional benefits that include:
- Clarity: Reviewers of specifications can easily assess the scope and type of work associated with a project.
- Efficiency: Information is quickly retrieved using this convenient hierarchical system as a roadmap.
- Compliance: Adhering to MasterFormat helps ensure construction projects comply with relevant regulations and standards.
Perhaps the greatest unforeseen benefit has been the smooth transition between traditional paper and electronic specification documents. MasterFormat has created an anchor for software adoption in North America by migrating the familiar and functional “filing system” into electronic databases and software tools.
Structure of the CSI MasterFormat
The ingenious MasterFormat structure has gained acceptance and nearly universal adoption in the North American construction industry. The format is easier to understand when you review the purpose, contents, and relationships of each individual level.
MasterFormat Divisions
The hierarchy begins with the 50 MasterFormat divisions (00 through 49) used to divide documents according to the area of construction they pertain to. Original divisions, including concrete, masonry, and metals, have now been joined by site, infrastructure, and process equipment divisions, such as transportation and waste control. Each division is defined by the first two digits of the six-digit MasterFormat code.
MasterFormat Sections
Within each division, there are multiple sections that further divide construction specifications based on materials and processes. For example, the concrete division (03) includes sections for precast concrete, structural concrete, low-density concrete, and many other options, each with a unique 2-digit code. These digits are the third and fourth numbers found in the overall code.
Subsections
CSI MasterFormat includes a third level for specific subsections to provide even more granularity for complex projects with many tasks and particular processes. Using our concrete example, the structural concrete section includes subsections for heavyweight, lightweight, high-performance, and ultra-high-performance varieties, among others. The last two digits in the MasterFormat code indicate the subsection. If no subsection is included, the last two digits are left as “00.”
Decimal level
Some MasterFormat sections have too many options to capture at one level, even when broken into subsections. In these cases, a decimal point is added after the sixth digit to create another categorization level.
For example, a rack mounted computer room air conditioner is defined by the division for HVAC (23), the section for decentralized HVAC (81), the subsection for computer room air conditioning (23), and the decimal for rack-mounted units (.16). In this case, the complete CSI MasterFormat code appears as:
23 81 23.16
This multi-layered format is ideal for software-based systems that allow contractors, clients, architects, and other stakeholders to quickly navigate to the correct section and drill down to the information they need.
CSI MasterFormat Divisions
CSI showed remarkable foresight over two decades ago when they created a system expansive enough to endure for over 20 years without requiring increased divisions. In fact, many divisions are still available for expansion. The complete list of divisions in 2025 is as follows:
00: Procurement and Contracting Requirements
01: General Requirements
02: Existing Conditions
03: Concrete
04: Masonry
05: Metals
06: Wood, Plastics, and Composites
07: Thermal and Moisture Protection
08: Openings
09: Finishes
10: Specialties
11: Equipment
12: Furnishings
13: Special Construction
14: Conveying Equipment
21: Fire Suppression
22: Plumbing
23: Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
25: Integrated Automation
26: Electrical
27: Communications
28: Electronic Safety and Security
31: Earthwork
32: Exterior Improvements
33: Utilities
34: Transportation
35: Waterway and Marine Construction
40: Process Integration
41: Material Processing and Handling Equipment
42: Process Heating, Cooling and Drying Equipment
43: Process Gas and Liquid Handling, Purification and Storage Equipment
44: Pollution and Waste Control Equipment
45: Industry-Specific Manufacturing Equipment
46: Water and Wastewater Equipment
48: Electrical Power Generation
MasterFormat Applications
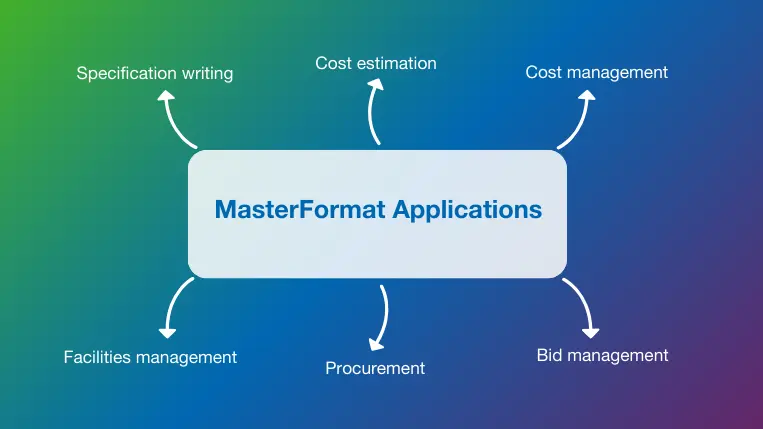
CSI MasterFormat has remained a fixture of the construction industry in North America for decades. The system’s versatility is evident by its many applications.
1. Specification writing
The original purpose of the MasterFormat divisions was to create an efficient system for specification writing and organization, and that purpose has continued to the present day. Specification books are often thousands of pages long; each specification is integral to the project’s success. MasterFormat provides the structure needed to create and organize concise three-part specs that improve efficiency and eliminate confusion and delays.
2. Cost estimation
The organized and logical structure of CSI MasterFormat supports the construction cost estimation process by breaking down projects into itemized work elements, with MasterFormat codes serving a dual purpose as standard cost codes to categorize the array of costs included in a typical project. This common data environment (CDE) also makes the information more visible and accessible to all project stakeholders during the estimation process.
3. Cost management
MasterFormat divisions provide a convenient format for effective construction cost management throughout the project. For example, when contractors utilize a schedule of values for billing purposes, these costs can be applied and tracked more easily by aligning them to the corresponding division. The granularity of MasterFormat creates an appropriate framework for comparing project budgets and estimated costs with actual costs throughout the project, as well as reporting on cost performance and trends by division and section.
4. Bid management
Each of the construction specifications organized by division, section, and subsection represents a corresponding bidding opportunity for qualified contractors or suppliers. This natural synergy makes it easier to collect and organize bids for each work item, then review the bids to ensure the details and intent of the specification were understood. Owners and clients can quickly identify bids that appear misaligned with other contractors or the specification itself.
5. Procurement
Procuring materials, tools, services, and equipment is another facet of construction that aligns perfectly with the MasterFormat structure. The construction procurement process involves defining requirements, comparing prices and vendors, and monitoring deliveries and other issues. Organizing procurement tasks based on appropriate sections and divisions is a great way to ensure all necessary procurement tasks are completed, while making it easier to assess and report on progress in harmony with other project management activities.
6. Facilities management
Once the construction phase is completed, CSI MasterFormat leaves behind a useful library of information to support operational activities like facilities management and maintenance. Installation instructions, replacement part information, and safety recommendations in construction specifications can save facilities teams valuable time during repairs, troubleshooting, and minor refurbishment tasks.
Conclusion
CSI MasterFormat has endured as a North American industry standard for over 35 years and is poised to remain the common language of construction codes and divisions for decades to come. Construction specification software like RIB SpecLink has taken MasterFormat into the digital age, making searching, modifying, and tracking specs and other important information easier.
As the exclusive CSI Software Platinum Partner, RIB SpecLink integrates over 1,000 broad and medium-scope CSI MasterFormat sections, enabling users to access a vast library of standardized content. Additional features for smart linking automatically manage the inclusion and exclusion of sections based on user selections, making specs error-free, collaborative, and extremely accurate.
If you want to benefit from a library of up-to-date content, a robust BIM integration, and a range of other functionalities that will skyrocket spec management, get your free trial for RIB SpecLink today!
Get My Free RIB SpecLink Trial Now
Most Recent
11 mins read
10 mins read
10 mins read
29 mins read
Blog Categories

Ebook