10 mins read
From 3D to 6D and Beyond: Understanding BIM Dimensions
Though the construction and engineering industry is infused with high-tech, when we discuss digital construction, we primarily refer to implementing BIM – Building Information Modeling – one of the most promising developments in the AEC (architecture, engineering, and construction) industry. With BIM, the boundaries between the physical and virtual spheres are merging, and how we plan, design, construct, and operate building projects is changing.
BIM has long been seen as integral to our industry’s future. This transformative technology has many supporters worldwide, with adopters pointing to improved speed of delivery, efficient collaboration, reduced costs and wastage, and long-term insights as key benefits.
A study by McGraw Hill Construction found that 75% of those who adopted BIM reported a positive return on their investment. They also reported shorter project life cycles and savings on paperwork and material costs.
With those positive numbers, it is impossible to ignore the value of this technology. But how does it actually work? We already discussed the history of BIM in a previous blog post; now we will take it one step further and discuss BIM dimensions.
Let’s dive in!
What is BIM?
The BIM Handbook defines BIM as “a modeling technology and associated process to produce, communicate, and analyze building models.” The concept has existed since the 1970s, and in the late 1970s and 1980s, the first software tools for modeling buildings were developed.
Simply put, BIM is a technology that enables multi-dimensional models of construction and engineering projects to be constructed in a virtual simulation before they are built in the field. It is based on a shared understanding of data content and structure. AEC industry professionals use BIM to efficiently manage building projects and gain higher productivity and better outcomes.
The use and evolution of BIM has seen rapid growth, particularly in the last decade. The latest BIM report by NBS showed that 73% of construction professionals use BIM, a big increase since a decade ago when only one in ten professionals used it.
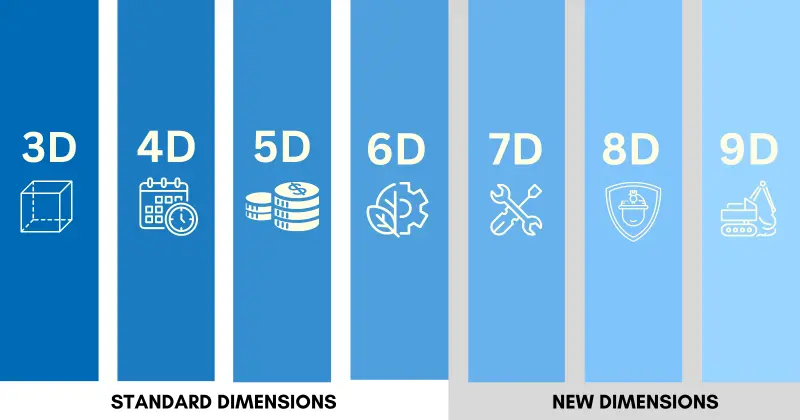
Over the years, BIM has evolved from simple 3D models to 6D BIM and beyond, populating the building model with information from different dimensions. This helps construction teams access and analyze the impact of major or minute changes in the project.
These dimensions have taken BIM projects to a whole new level by offering a 360-degree view of all project aspects in a centralized location, boosting collaboration, accuracy, and productivity. Let’s explore each of these dimensions below!
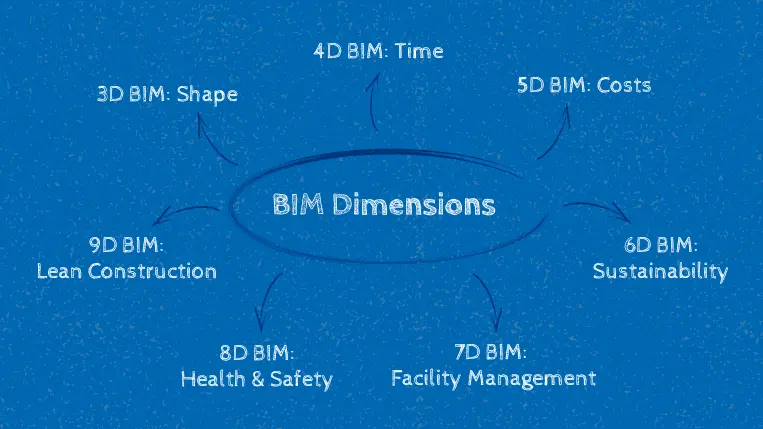
3D BIM: Shape
The 3D BIM dimension is probably the most popular one. It represents a building’s geographical structure. Think of it as a more complex version of 2D drawings, but instead of just having the traditional X and Y-axis, you add a third X-axis. The 3D BIM model allows construction companies to visualize their projects with all their elements, including beams, walls, floors, mechanical equipment, and physical properties. Such an overview helps automate tasks, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency.
Benefits include:
- An accurate 3D visualization of the entire project for accurate decision-making
- Enhanced communication and collaboration between project stakeholders thanks to a common data environment (CDE)
- Reduces the need for reworks due to enhanced transparency from preconstruction to completion
- It allows for the automation of several tasks, such as clash detection, saving the project a lot of time and money
4D BIM: Time
The 4D BIM dimension adds a time layer to the 3D model. It integrates work stages and their duration to create a model-based schedule and process plan. Schedule data connected to a 3D project overview allows project managers to better plan by understanding how the design and time components work together. 4D BIM also allows for the simulation of different timelines to see what works better for the project.
Benefits include:
- Significantly enhance on-site planning to ensure every stage during construction runs smoothly
- The ability to identify potential scheduling issues and tackle them to reduce risks
- Enhanced safety thanks to a plan with specific timelines
- Better communication and efficiency of stakeholders as tasks and time are clearly defined
5D BIM: Costs
The 5D BIM dimension adds additional cost data to the 3D model. This allows for efficient construction cost estimation and budgeting by accurately forecasting costs based on the project’s materials, labor, and other aspects. When a building project’s 3D design is integrated with “time factor” (4D) and “cost factor” (5D), it’s much easier for project stakeholders to understand what’s being built, how, when, by whom, with what, and at what cost and provide quick feedback.
Benefits include:
- The ability to explore multiple model-based cost scenarios to ensure that the design being considered is within the budget
- Real-time cost reporting to avoid budget overruns and other cost-related issues
- Enhanced accuracy thanks to costs being updated every time there is a change in the model
- The possibility of automating the quantity takeoff process to eliminate manual tasks and minimize errors
6D BIM: Sustainability
What Is 6D BIM?
The 6D BIM dimension integrates environmental data into the 3D model, allowing decision-makers to monitor and optimize the project’s environmental impact. The data tracked includes energy usage, air quality, embodied carbon emissions, water usage, and much more.
With 6D construction simulations, the 3D design model is integrated with the schedule (4D), cost (5D), and sustainability factor (6D), allowing stakeholders to compare different design options side by side, optimize the project from every angle, balance cost, schedule and now, the impact on the environment.
For instance, measuring the amount of embodied carbon within production materials helps construction project teams evaluate a project’s overall carbon emissions. They can then utilize that information to procure low-carbon material alternatives or, in the case of regulators, set embodied carbon limits.
Before integrated platforms were available, this was done by the ‘big-room collaboration’ methodology, where key stakeholders sat in the same room with whiteboards and sticky notes. From there, they discuss the potential challenges and issues that might pop up during the project execution and try to alleviate those constraints before pitching a shovel on the site. Luckily, this is no longer necessary thanks to 6D BIM models, which offer a single source of truth to make all project decisions accurately and fast.
Let’s explore some benefits below!
Benefits Of 6D BIM For Sustainable Construction

Gain higher efficiency by:
▷ Working in a model-based way with your teams and partners.
▷ Creating added value in compliance with costs and quality for your client.
▷ Optimizing conventional planning for further execution.
▷ Integrating data sources.
Become more sustainability-friendly because:
▷ You can reduce wastage and resources by optimizing planning with 6D.
▷ You can select green materials using intelligent business partner management and enhanced procurement processes.
▷ By optimizing your supply chain, you can reduce carbon emissions from the transportation of materials and equipment.
▷ You are equipped with end-to-end product environmental footprint calculation and qualification.
▷ You open the door to other buildings in the future.
Why should construction companies care about sustainability?
We spend 90% of our time in the buildings where we live, work, learn, entertain, and produce things. But have we ever stopped to think about the impact that these buildings have on our planet? The CO2 emissions of the giant industry we interact with every day – building and construction – have increased to their highest levels to date, representing 38% of global energy-related CO2 emissions. As an industry that employs 7% of the world’s working-age population and as 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by 2050, stakeholders in this industry must take responsibility to reduce emissions and create a sustainable and net-zero future for everyone.
We all care about a sustainable future, so we must work together to minimize or even avoid stressing our environment. If we want to meet the targets set out in the Paris Climate Agreement, the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector must be committed to environmental protection and a leader in moving towards decarbonization.
What does this mean for companies in this sector? Organizations that focus on sustainable building and construction can:
- Future-proof their business by providing a competitive differentiator in the market and remaining a step ahead.
- Be compliant with potential government regulations or restrictions on carbon emissions.
- Improve employer reputation and employee performance, thereby attracting and retaining future talents.
- Save costs from less waste and more energy-efficient building operations, making the most of natural resources and renewable energy.
- Invest in the right technologies to boost construction sustainability and decrease carbon emissions.
Sustainability is a journey
Depending on where your business is on the digitalization journey, we can all agree on one thing: the power of the almighty certification stamp to satisfy the requisite authorization from higher entities. However, this is nothing more than motivation; indeed, inspiration comes with motivation.
Sustainability, therefore, is a journey that propels our industry to new endeavors, reach new heights, and do things differently. Technology is the enabler that will help drive more and more businesses to place sustainable practices and technologies as one of their core processes. VDC (Virtual Design and Construction) tech and IPD (Integrated Project Delivery) methodology are examples of these technologies and practices as they allow us to build virtually before executing physically, optimizing a project not only from the financial, scheduling, procurement, and risk management point of view. They can immediately save not just time and money but also reduce waste and, in some cases, enormous amounts of waste. By placing sustainability in your business as a core process, waste, emissions, and your carbon footprint can all be dramatically cut from the building process.
Sustainability and environmental, social, and governmental (ESG) goals should not be peripheral to your business strategy. They should be embedded in the company so that they impact the way you think, act, and do business. This paradigm shift can enable an organization to embed sustainability into its products and services, how it caters to its clients, and how it manages its organization and stakeholders.
What Can 6D BIM Sustainability Software Do For You?
How can enterprises in the construction industry achieve a sustainable future without compromising their productivity? Our answer: digital transformation – transforming how we plan, build, and operate our buildings. To this end, RIB’s flagship construction management platform, RIB 4.0, is adding the 6th Dimension – the carbon factor – to its 5D BIM (Building Information Modeling).
RIB 4.0 connects all people, processes, and data from project concept to completion to break silos, maximize efficiency and achieve sustainability. Many decisions will inevitably impact project efficiency and energy consumption when designing a building project. RIB 4.0 enables 6D simulations of different design options, in which the 3D design model is integrated with the schedule (4D), cost (5D), and carbon factor (6D), enabling teams to compare options side by side and optimize the project.
Let’s explore some of the key features of our software below:
- Built-in object library for carbon calculation
The object library in the RIB 4.0 master database has over 100 datasets associated with carbon and Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) from Europe, North America, and Asia Pacific, and the list is growing. By creating a quantity in RIB 4.0, all the work packages can be monitored to avoid material waste. Quantifiable not only in time and cost but also in carbon, be it embodied carbon or carbon created in the process, the object library links with the cost libraries.
- Qualify material suppliers to minimize embodied carbon
Material suppliers, logistics vendors, contractors, and building users on the RIB 4.0 platform will give project leaders much better visibility of the design options, materials, and process choices that can then be quantified, optimized, and monitored for their carbon emissions throughout their lifecycle, from the construction procurement phase to the operation and maintenance phase.
- Carbon tracking and control using dashboards
The RIB 4.0 Control Tower provides dashboards that give an overview of an enterprise’s projects. The wider stakeholders have real-time access to information to be more proactive than reactive when managing projects. The platform gives early warning indicators so teams can find ways to rectify and solve issues before a larger and more serious negative impact materializes. The dashboard displays embodied carbon, assisting in optimizing the lifecycle sustainability of that asset.
- Open API allowing for third-party software
Different tools are available in the market that do excellent energy optimization. RIB 4.0 retains an open front end towards these design inputs as an open platform for the wider supply chain. Embodied carbon data is available in RIB 4.0 with its built-in object library and open API.
Other BIM Dimensions: 7D, 8D and 9D
The BIM dimensions mentioned previously are widely recognized in the industry, and multiple software solutions include them in their offerings. That said, the BIM industry is still developing, and new dimensions are emerging to keep enhancing this technology’s power. Let’s discuss three less-explored BIM dimensions below!
7D BIM: Facility Management
As suggested above, the 7th dimension of BIM is related to the management and operation of the building. It gathers data like maintenance and operation manuals, technical specifications, warranty information, asset management, and much more to ensure all relevant knowledge on managing the facility is easily accessible within the model.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced facility management from design to demolition thanks to a central point for all relevant documents and information
- It makes maintenance and repairs easier throughout the entire project lifecycle
- The possibility to analyze the operational performance of different components of the building for early detection of issues and setting up proactive maintenance to enhance asset longevity
8D BIM: Health & Safety
Moving on to a less explored dimension, 8D BIM focuses on health and safety. This dimension was born out of the importance and need for safety in construction sites, where incidents are an everyday occurrence. An 8D model allows for enhanced risk identification from the early stages of the project, enabling the company to mitigate risks or prepare for them in case they happen unexpectedly.
Benefits include:
- Significantly reducing the possibility of accidents on the building site
- Better planning of safety strategies thanks to risk predictions
- Make design decisions in the context of safety
- Possibility to train workers about potential safety risks and how to tackle them
9D BIM: Lean Construction
Lastly, the 9th dimension of BIM focuses on lean construction. Lean construction is an approach that optimizes the management and design of a building instead of just focusing on the end product. It basically aims to maximize the value of each construction stage while keeping waste to a minimum. A successful lean construction process relies heavily on collaboration, making BIM the perfect tool to carry it out.
Benefits include:
- A 9D model helps to maximize productivity and minimize waste thanks to a mix of design (3D), time (4D), cost (5D), sustainability (6D), maintenance (7D), and safety data (8D)
- Helps optimize resource management by standardizing processes
- Enhanced communication between stakeholders, which prevents costly errors and enhances transparency and quality
Final Thoughts
Here at RIB Software, we’re driven by disruptive digital technologies, industry best practices, and trends. We have made it our purpose to propel the industry forward and make engineering and construction more efficient and sustainable. That includes supporting the development and availability of world-leading solutions that empower industry professionals to quantify, measure, report on, and compare embodied carbon across the project lifecycle.
And we’re not stopping there. In-progress development sees our solutions ultimately enabling better design and procurement decisions that factor in cost, time, and carbon to mitigate and eliminate embodied carbon used across a building’s life.
If you are ready to experience the power of professional BIM management software and boost project efficiency and profitability, get a demo of RIB products today!
Most Recent
10 mins read
11 mins read
11 mins read
10 mins read
Blog Categories

Ebook










