10 mins read
Exploring Key Green Design Concepts, Principles & Examples

As global awareness of environmental issues rises, the construction industry embraces green design principles to create more sustainable and energy-efficient buildings. Green design goes beyond visual appearance by reducing the environmental impact of structures throughout their entire lifecycle. By focusing on resource conservation, energy efficiency, and waste reduction, green architecture helps preserve the planet’s natural resources and enhances the well-being and efficiency of building occupants.
Keep reading to learn everything about this important topic!
What is Green Design?
Green design is a comprehensive process intended to minimize the designed infrastructure’s environmental impact and energy consumption. Green design principles incorporate material selection and construction options that slow down natural resource depletion.
The concept of ecologically sound or “green” architecture originated in the 1960s, and the world’s first green building standard was introduced in the UK in 1990. Green designs consider the enormous number of natural resources and waste that go into constructing and operating buildings, factories, stadiums, and other structures. Reversing these trends requires an approach that includes architecture, landscaping, and urban planning.
Benefits of Green Building Design
The buildings we inhabit provide a great opportunity to minimize the impact of human activity on the environment while improving our own quality of life at the same time. Green building design brings many important benefits, including:
- Enhanced health and safety: Green buildings use materials that are friendly to the environment and people. That means avoiding building materials that contain harmful byproducts and toxins. For workers, green designs also promote mental and physical well-being by incorporating natural lighting, green spaces, and ergonomic layouts.
- Reduced waste: Green designs minimize waste from the design phase throughout the building’s life. This begins with renewable, recycled, and reused raw materials for construction and continues with features like water purification systems to reduce water consumption and high-efficiency insulation to minimize heating and air conditioning waste.
- Reduced operational costs: Reduced material and utility expenses contribute to the overall reduction in operational expenses, which includes building maintenance, repairs, and waste management. The average operating cost savings in the first year for new green buildings is -10.5%.
- Increased efficiency: Renewable building materials and energy sources used for green construction design provide a win-win by reducing environmental impact and CO2 emissions while making the building more energy-efficient and cost-effective. Upfront costs for design elements like solar panels and green roofs are quickly recovered through savings on energy over time.
Top Green Design Principles
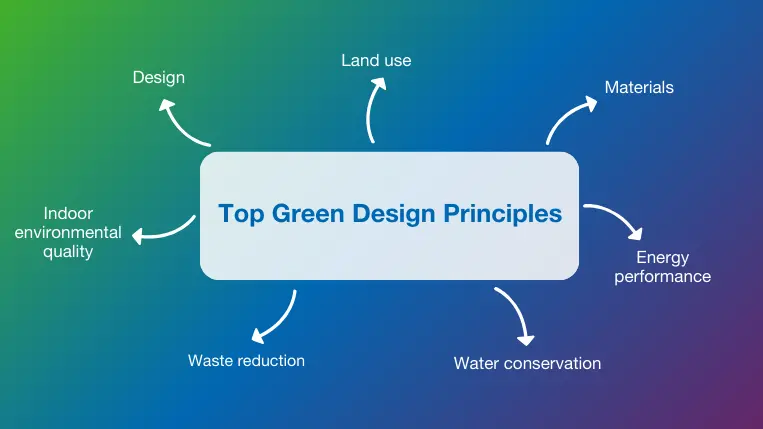
Green building design concepts may seem intuitive, but designers and architects need to follow a set of guiding principles to optimize their results. These principles fit into several overall categories that summarize the goals and objectives of green design.
Design
Many green design objectives stem from the design and architecture of the building itself. This includes incorporating concepts like biophilic design, which focuses on connecting building occupants to nature, and innovative multi-purpose areas, which reduce space and resource consumption. Overall design considerations include basic ventilation, lighting, and window installation options, which support other green design principles.
Land use
Minimized land use is one obvious green objective, but land use considerations also include reduced interference with native plants and wildlife, effective stormwater runoff, transportation to and from the location, parking, and sustainable landscaping possibilities that further minimize the environmental impact.
Materials
Green design principles for material selection begin with maximizing the use of recycled and reusable building materials during construction. This key design principle also extends to things like low-impact concrete production, sustainable sourcing of lumber products, and toxin-free insulation materials.
Energy performance
With the operation of buildings responsible for 30% of all global energy consumption, energy efficiency is another fundamental pillar of green design architecture. Opportunities to reduce energy consumption through green principles come from smart lighting and heating systems, energy-efficient windows, and the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the building design.
Water conservation
With more people, agriculture, and buildings around the world, water is becoming an increasingly scarce resource. Along with water purification systems to encourage reuse, green principles call for the use of more water-efficient fixtures, faucets, and plumbing to prevent water from being wasted.
Waste reduction
By continually seeking out new ways to minimize waste in everything from building materials and construction processes to electricity and water consumption, green designers can build efficiency into new structures from the ground up, rather than asking occupants or workers to make dramatic changes to their habits.
Indoor environmental quality
The use of green design architecture will expand if the indoor environmental quality (IEQ) of new buildings continues to support occupant health, safety, and productivity to increase the demand for these practices. Improved air quality, natural light, and the use of green spaces can make these modern buildings more conducive to overall comfort, health, and stress reduction.
Green Design Examples
Impressive green design examples appear each year, with new projects building on previous designers’ ideas. Recent achievements in green building design have shown us how the world’s most unique and visually appealing structures can also be eco-friendly and energy efficient.
Pixel Building (Australia)
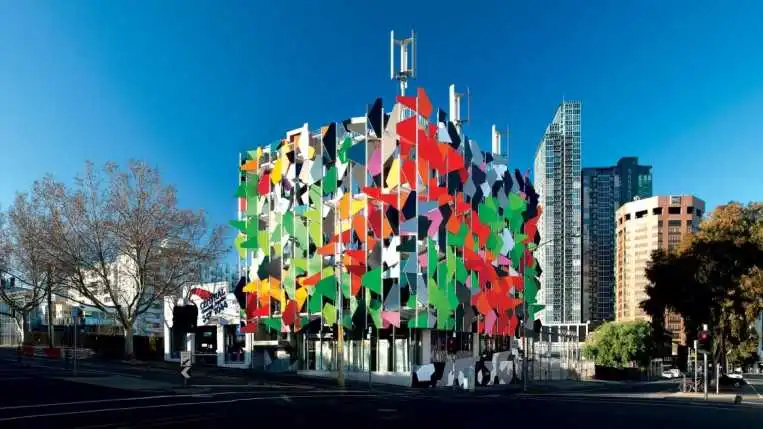

This visually stunning office building in Melbourne, Australia, illustrates how a design concept can deliver on multiple green fronts. The unique panels lining all surfaces of the building provide natural shade to cool occupants and then help capture rainwater to improve efficiency in other areas. Vertical wind turbines on the roof blend in with the unique building appearance while helping to make the Pixel building the first carbon-neutral office building in Australia.
Ayedemi Floating School (Nigeria)
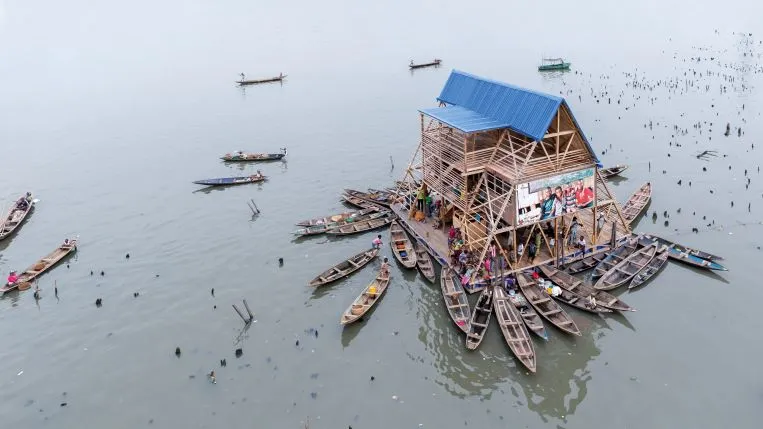

Architect Kunlé Ayedemi more than rose to the challenge when it came time to design and build a sustainable school in one of the most flood-prone areas of Africa. The flexible and buoyant foundation made use of recycled plastic barrels, while the structure itself leveraged locally sourced wood and bamboo. Despite the constraints of the rain-soaked terrain, solar panels were also incorporated to provide a reliable off-grid energy supply.
VIP Structures Headquarters (New York)
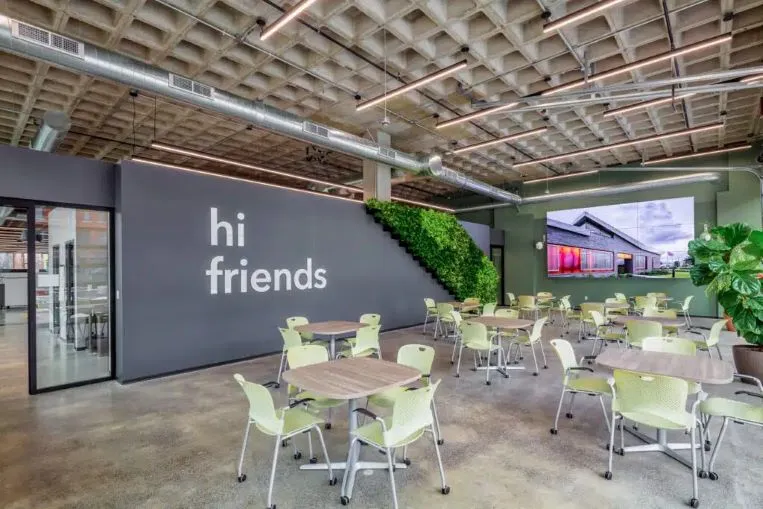

VIP Structures’ new office headquarters in Syracuse, New York, is one of the best examples of green design in the United States. Occupation-censored lights that turn off when spaces are empty, gray water recycling, radiant floors, and multi-control HVAC show the impact technology is now having on green design practices. The building also emphasizes clean indoor air and inviting break spaces to promote occupant health and productivity.
How to Achieve Green Designs
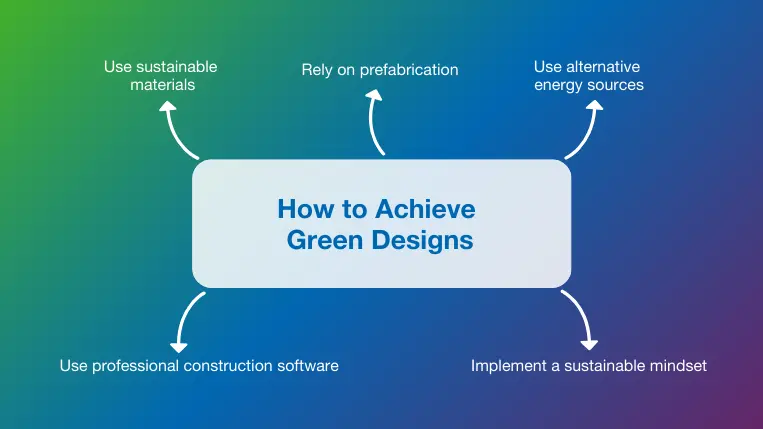
Adhering to basic green design principles provides a pathway to success, but a few key concepts and practices can ensure the design is sustainable, efficient, and functional throughout its lifespan.
- Use sustainable materials: Green building materials include those that can be (or already have been) reused or recycled, but they also include materials like bamboo and cork that can be grown and harvested with little environmental impact.
- Rely on prefabrication: Off-site construction (prefabrication) is performed in climate-controlled factories that make it easier to incorporate sustainable materials. During construction, prefabrication reduces trips to and from the job site and speeds up project times to reduce emissions. Standard prefabbed modules also lend themselves well to reuse when buildings are reconfigured. If you want to learn more about this topic, check out our guide on precast concrete.
- Use alternative energy sources: Our green design examples and many other projects around the world have built sustainable energy sources like wind and solar into the infrastructure. This early focus makes planning for and achieving net zero or carbon-neutral status possible from day one. Using carbon estimating software is a great way of measuring the success of these initiatives and finding improvements.
- Implement a sustainable mindset: Green building design concepts must be implemented into all construction project phases to be successful. Designers should incorporate the underlying goals of environmental responsibility, resource conservation, and waste reduction into every decision. Implementing a construction change management plan is a great way to implement green principles at an organizational level.
- Use professional construction software: Turning green designs into reality requires accurate material estimates, ongoing collaboration, and attention to detail. Professional construction software streamlines these processes through cloud-based tracking, reporting, and communication. RIB CostX, our estimating and BIM takeoff software, helps designers, clients, and builders perform accurate quantity takeoffs and estimates from 3D BIM models and other digital formats. A carbon estimating module helps green designers assess their projects by calculating the embodied carbon and total carbon output.
In Conclusion
As housing, office buildings, and factories expand their footprint to accommodate more occupants, green building design is quickly becoming necessary. Innovative new structures and materials make relying on manual construction management and estimating practices impossible. The advanced takeoff, estimation, and reporting capabilities of RIB CostX have been developed with green design principles in mind, building on the efficiency and technology of successful new projects.
If you are ready to transform how you design, construct, and manage your projects, get a free demo for RIB CostX today!
Most Recent
10 mins read
10 mins read
11 mins read
10 mins read
Blog Categories

Ebook