11 mins read
An Overview of Specifications: Key Definitions, Benefits & Types

From construction and manufacturing to healthcare, tech, and product design, specifications ensure consistency, quality, and compliance by defining exactly how something should be built, installed, or operated.
In this blog, we’ll explore the concept of specifications, their role in different industries, the various types found in each sector, and much more.
Let’s dive in!
What are Specifications?
Specifications, or specs, are detailed documents that define the guidelines and requirements for a product, system, or service. They contain key information about how something should be constructed, implemented, or operated to meet quality and safety objectives.
Specifications contain information that changes from industry to industry. However, they are generally explicit requirements, such as raw materials, ingredients, formulas, packaging, workmanship, machinery, legal requirements, and any other technical detail that people working on that product, service, or project need to know.
These documents serve as invaluable communication tools for contractually bound parties, outlining the expectations for the finished product. Having a complete, precise, and standardized overview helps avoid legal disputes and ensure the highest-quality results.
Who Uses Specifications?
Construction: Construction specifications describe the materials, systems, equipment, workmanship, and regulatory requirements to bring a building to life in the expected time, budget, and quality. They also ensure all parties are on the same page, avoiding rework and legal disputes.
Manufacturing: Likewise, manufacturing specifications outline product design, material tolerances, production methods, assembly instructions, testing procedures, and other relevant information. They help support quality control and reduce errors during fabrication.
Software development: Specs document technical and functional requirements for software, hardware, or systems. They are essential for guiding development teams, ensuring interoperability, and avoiding miscommunication.
Automotive & transportation: The specifications in the automotive and transportation section ensure that all elements, systems, and parts meet safety, performance, compatibility, and regulatory standards. They include valuable information, including engine, transmission, dimensions, and fuel economy, among many others.
Consumer Goods & Packaging: Specs for this industry define packaging materials, labeling requirements, shelf life, and product dimensions. They help ensure consistency, quality, and safety, protecting products and customers and building brand trust.
These are just a few of the many industries that benefit from specifications. But what makes these documents so valuable today?
Benefits of Using Specifications
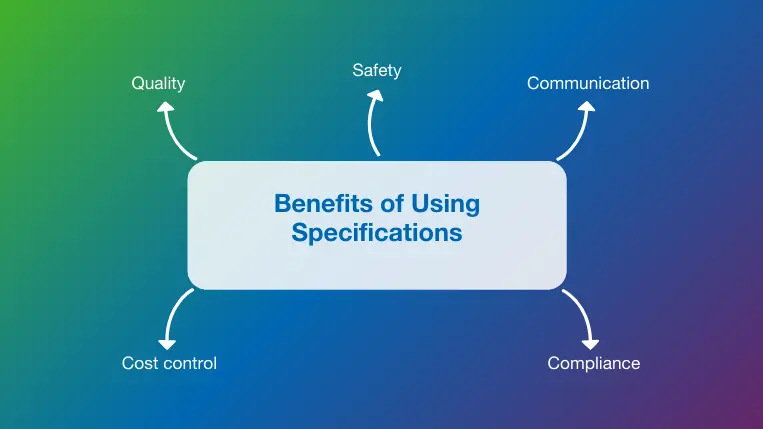
Specifications are invaluable across industries to communicate crucial technical and operational information clearly and effectively. Some tangible benefits from specs include:
Quality: Effective quality assurance and control are arguably one of the most significant benefits of specifications. Having a detailed outline that includes all the necessary information to bring a project or product to life ensures that deliverables meet client expectations and regulatory requirements. For instance, in construction, specs are used to support quality control inspections, reducing the risk of costly rework.
Safety: Another fundamental benefit of specifications is that they enhance safety by clearly outlining the processes, standards, and materials needed to avoid accidents or potential hazards during production, construction, and subsequent use or operations. They detail acceptable practices, safe installation methods, and other safety benchmarks to ensure everything runs as expected.
Communication: Specifications provide a clear, standardized way to convey project requirements, reducing ambiguity and misinterpretation. They act as a shared information hub that ensures all stakeholders are aligned, improving collaboration and minimizing conflicts that can lead to more significant issues.
Compliance: Specs ensure that a product, service, or system complies with any industry or governmental regulations or standards, including building codes or the CSI MasterFormat for construction or the FDA for healthcare. This helps prevent non-compliance issues that can significantly delay a project and cost it a lot of money.
Cost control: By clearly outlining the scope of work, materials, workmanship, performance standards, and any other details depending on the industry, specs accurately support resource allocation and budgeting. This precision helps avoid budget overruns due to uninformed procurement processes or miscommunication from stakeholders.
Types of Specifications

As you’ve learned by now, specs are used across several industries. Each industry has a different purpose and end goal; therefore, many types of specs exist to meet those goals. The most common ones are:
Technical Specifications
Technical specs, mainly relevant to construction and manufacturing, describe how a product, system, or service should be built or implemented. They provide detailed information about materials, installation processes, construction methods, compliance standards, safety procedures, and much more. They guide contractors, manufacturers, and several other relevant stakeholders on how the work should be done.
Functional Specifications
Functional specifications define what a product or system should do. Unlike technical specs, functional specs focus on what the product should accomplish instead of how, detailing the intended user experience, interactions, and outcomes. These specs are usually relevant in software development, engineering, and product design, providing a roadmap for performance expectations.
Product Specifications
These specs describe the physical and functional attributes of a finished product, including dimensions, weight, relevant components, performance standards, features, and tolerances. They are relevant for industries like retail, automotive, electronics, and others that must deliver quality products that meet regulatory requirements and client expectations.
Design Specifications
Design specs detail the aesthetics, functionality, layout, ergonomics, and materials of a product, system, or building. They are commonly used in architecture, construction, industrial design, and product development, helping ensure the final result aligns with design intentions.
Material Specifications
As its name suggests, material specs offer invaluable information about raw materials used in construction projects or product manufacturing. They often include details about strength, durability, safety, thermal properties, and compliance with codes and regulations. They help reduce risk, ensure quality and safety, and streamline procurement processes.
Performance Specifications
These specs outline the expected performance outcomes for a project or product, like strength, efficiency, speed, or durability, without explicitly dictating how to achieve them. They are mainly used in construction, manufacturing, and technology development when the client wants to encourage contractors or suppliers to deliver innovative, cost-effective solutions.
Test Specifications
These documents list the methods, criteria, and standards that must be followed to test a product or system. They detail the test methods, tools to be used, conditions under which the test should be carried out, success criteria, and guidelines for reporting the results. They are invaluable tools for quality control and are mainly used in industries like electronics, construction, and pharmaceuticals.
Packaging Specifications
As inferred from the name, packaging specs outline the requirements for how a product should be packaged, stored, and labeled. They include information about the materials for the packaging, weight limits, environmental implications, safety labels, container dimensions, and more. Industries like food, retail, and logistics use them to reduce damage during packaging and transportation, support branding, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Reference Specifications
Commonly used in construction, design, manufacturing and engineering, reference specs cite recognized standards and codes to outline quality, testing, and performance requirements. Instead of explaining all the technical requirements in detail in a lengthy document, it tells you what standards to follow to ensure compliance.
Common Specification Challenges & How to Solve Them
Specs are technical documents that require high attention to detail and technical knowledge to develop. Some common challenges found across industries include:
Ambiguity: One of the most common challenges when developing specs is ambiguity. Given the technical nature of the content, the person in charge of writing it might use overly complex language or too vague descriptions, assuming everyone who reads them will have the same level of knowledge. This can lead to costly mistakes and legal issues that are difficult to solve. Organizations should adopt a standardized approach to spec writing to avoid this issue, ensuring a clear, simple, and understandable language is used across all documents.
Outdated information: In most industries, specs are not a “done and dusted” kind of job; they require ongoing updates as materials, standards, or references can quickly become outdated. This challenge occurs frequently in the construction industry, where changes occur daily and version control issues can lead to costly errors. To avoid this, companies must invest in professional specifications software for dynamic content updates and automated syncing across documents, ensuring users consistently access the most current, approved information.
Poor collaboration: In many projects, specs are written in isolation by different departments or external consultants, leading to silos and communication breakdowns. This can result in duplicate work or misaligned deliveries, leading to significant issues later on. Innovative specifications platforms offer powerful features like access controls, comment threats, and web-based access, ensuring seamless collaboration and a shared understanding among stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
Specifications are potent documents that convey crucial information to bring projects, products, or systems to life. They clearly communicate the scope of work, technical and operational data, and many other details you learned from this blog. Construction is one of the industries that benefits the most from well-written specs, as they serve as the “instruction book” for how the work should be done, connecting contractors, architects, engineers, clients, and any other stakeholder through a single source of truth, reducing the risk of rework and boosting project quality and profitability.
Professional specifications software like RIB SpecLink has become the biggest ally for manufacturing, construction, and architectural specs. Our robust platform uses the power of BIM, automation, and cloud-based technologies to offer innovative functionalities that take the spec writing process to the next level, eliminating manual edits, boosting collaboration, and significantly cutting the time it takes to generate and edit specs.
If you want to benefit from reduced errors and omissions, increased productivity and collaboration, and a single source of truth throughout the specification lifecycle, get your free demo for RIB SpecLink today!

Most Recent
11 mins read
10 mins read
10 mins read
29 mins read
Blog Categories

Ebook