10 mins read
Construction Scheduling: See Concepts, Benefits, and Industry Best Practices

No project can be successful without first defining success and establishing a plan to achieve it. Realistic and accurate construction planning requires considerable research, scheduling, and collaboration, but the extra effort pays off when high-quality projects are completed on time and on budget.
In this blog post, we review the benefits and basic elements of construction scheduling to shed more light on this critical topic. We also look at some of the established principles, methods, and best practices behind the most successful construction project schedules.
What Is Construction Scheduling?
Construction scheduling is a detailed process that involves the creation of a timeline with all project activities, resources, and milestones included. The construction schedule becomes a living document to guide and prioritize task completion throughout the project.
The construction scheduler, responsible for preparing the schedule, must ensure all material, labor, and design issues are accounted for so that each activity can be completed on time and on budget. This requires planning skills, foresight, and close collaboration with project owners, designers, architects, contractors, and suppliers. Important elements of a construction schedule include:
- Task start dates to show the sequencing and prioritization of key activities
- Durations to indicate how long each task is expected to take
- Project milestones to capture critical events and deadlines
- Resource allocations to define contractor labor, equipment, and materials
- Lead times that show how long it will take materials and equipment to arrive
- “Floats” that indicate how long a given task can be delayed without impacting the entire project
Construction Project Scheduling Benefits
Construction project schedules bring many important benefits, including improved time management, optimized resource allocation, and effective budget tracking. Construction schedules also account for interdependencies between tasks to prevent downtime and interruptions. For example, the completion of interior electrical work must be closely timed to coincide with subsequent activities like pre-drywall inspections and drywall installation.
Schedules establish a baseline for comparison so that any discrepancies are identified quickly, and actions can be taken to mitigate issues to get the project back on track. A well-designed and accurate construction project schedule also acts as a communication tool that keeps all stakeholders on the same page and sets clear expectations.
Construction Scheduling Basics: Methods & Principles
Construction project scheduling is recognized as a valuable practice that prevents unexpected delays and overruns that can undermine project success. Many different methods have evolved to complete this process, each with unique features and benefits. Following a few basic principles to guide schedule creation and management can ensure that any commonly used scheduling methods yield accurate and useful results.
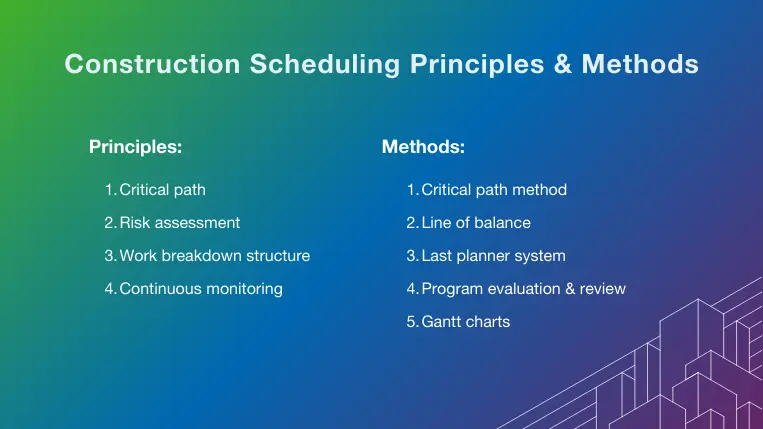
Construction Project Scheduling Principles
Schedule principles are the guidelines and best practices that have been developed over time to standardize practices between organizations and prevent important elements from being overlooked or misrepresented. The most important construction scheduling principles include:
Critical path
Once individual tasks and their durations and interdependencies have been mapped out, it becomes evident which ones are on the critical path, meaning their delay creates a ripple effect that can jeopardize the overall project completion date. Knowing what is (and is not) on the critical path helps construction project managers utilize time and resources more effectively.
Risk assessment
Risk assessments are completed in parallel with the construction scheduling process to identify issues and obstacles that have the potential to impact the timeline, budget, or quality of a project. Effective construction risk management strategies throughout the building process help to prevent unplanned or unexpected events from impacting the schedule.
Work breakdown structure (WBS)
Work breakdown structure is a construction schedule management principle that breaks tasks into more manageable and predictable pieces. The WBS hierarchy flows from the project level down to measurable work “packets” that can be accurately defined and measured.
By defining these compact and manageable work elements, WBS provides a clear framework to assign responsibilities and track progress. The hierarchical WBS principle reduces complexity while ensuring all project elements are included.
Continuous monitoring
Construction scheduling basics also include an understanding that schedules rarely remain static once they are created, so continuous monitoring to make sure activities are on track is at least as important as the initial schedule creation. Tracking progress daily through interactive construction reports and reviewing actual vs. planned performance is a recommended best practice. Any required changes or deviations should be discussed with relevant stakeholders immediately so that appropriate resource adjustments can be made.
Construction Scheduling Methods
The various methods that have evolved to make scheduling easier and more reliable each look at complex construction projects from a slightly different angle. These techniques share the common objectives of optimized resource management and improved time efficiency, which are the keys to project success.
Critical path method (CPM)
This method builds upon the value of determining the project’s critical path to ensure appropriate task prioritization and timely project completion. This approach is also valued for its simplicity and user-friendly format. The CPM method often relies on fixed durations and historical data, so it is important to account for uncertainties and continually update the schedule to reflect changes.
Line of balance (LOB)
The line of balance is ideal for construction schedules that include many repetitive or predictable tasks, such as a large row of identical tract homes. The LOB method graphically depicts scheduled work vs. actual work completed, using diagonal lines to clarify any deviations. For projects lacking unique tasks or complex interdependencies, this method helps to highlight any increases or decreases in productivity over time.
Last planner system (LPS)
The last planner system is based on lean construction principles that emphasize “pulling rather than pushing” of work to building crews. Using this method, project milestones are established first, then presented to contractors and team members so they can work backward from end dates to define appropriate start dates. This approach differs from more traditional workflows that sometimes force crews to compress their tasks into unrealistic timelines.
Program evaluation and review (PERT)
This technique uses statistical tools and analysis to compensate for uncertain or unpredictable task durations. The project team will estimate optimistic (best case), pessimistic (worst case), and most likely time allotments. These estimates are plugged into a standard formula to determine the most likely duration. The three estimates also allow a range of schedule scenarios to be generated to support projects with many unpredictable factors.
Gantt charts
These charts provide a familiar graphical view of construction job scheduling, including horizontal bars for task durations, diamonds for milestones, and arrows for interdependencies. A Gantt chart is a scheduling and planning tool that is not aligned with any specific method, so it can be used with CPM, LOB, PERT, and most other common schedule types. As an accepted and commonly used graphical tool, Gantt charts are ideal for communicating schedule information to clients, contractors, and other stakeholders.
Tips and Best Practices for Construction Schedule Management

While it is important to remain consistent with industry-standard construction scheduling methods and principles, some additional tools and practices should be considered to ensure the process is optimized for each project.
1. Set realistic timelines and milestones
Even though approximately 75% of construction projects experience delays, nothing undermines the effectiveness of a schedule faster than inaccurate or unachievable milestones. Contractors are likely to work under duress to meet deadlines or sacrifice quality for the sake of completion when timelines are not realistic, either of which can create unsafe working conditions. Inaccurate schedules call the credibility of the entire process into question. Recommended practices for creating more achievable and accurate timelines include:
- Collaborating with stakeholders to build consensus on expected durations
- Utilizing WBS principles to break projects into more manageable tasks
- Carefully reviewing historical performance for similar tasks
- Accounting for external factors like inspections, permits, and weather conditions
2. Choose the right methods and tools
The wide variety of available construction project scheduling methods is beneficial for teams searching for the format that best suits their needs, but selecting the right method is crucial. For example, a complex project with clear dependencies might be a natural fit for the CPM approach. In contrast, a project integrating new or unpredictable digital construction technology will likely benefit from the PERT technique.
The scheduling method selected is also a key factor when deciding on the appropriate construction software tools. The simplest of projects might only require basic Gantt chart templates. In contrast, complex projects with more tasks and interdependencies can be difficult to manage without dedicated construction scheduling software to organize essential information, manage resources effectively, and automate progress updates.
3. Allocate resources throughout the project
Effective resource allocation is what turns the numbers, bars, and symbols in a schedule into tangible results. Resource loading is the process whereby labor hours and costs are loaded into the schedule and linked to the contractors or suppliers assigned to each task. The resource allocation process should begin during the preconstruction planning stages and continue until all work is completed. Professional scheduling software is useful for continually tying resource allocation to the timeline and monitoring allocation vs. performance to determine when adjustments are necessary.
4. Plan for the unexpected
When it comes to building schedules, the only constant is change. Failing to plan for construction contingencies is one of the most common and costly scheduling pitfalls. Rather than creating arbitrary buffers as a catch-all for any unplanned events or delays, risk assessments and PERT analysis can be used to create more logical, data-driven contingency buffers that build more flexibility into the schedule. Planning for the unexpected upfront helps to avoid reactive strategies like schedule compression late in the project that can compromise work quality and drive up overtime costs.
5. Continually review the schedule
While there are no predefined construction scheduling management norms for review frequency, project managers and other stakeholders should monitor progress continually to ensure all tasks are tracked according to plan and surprises or delays are minimized.
Look-ahead schedules are a valuable tool for reviewing upcoming tasks in the short term. A look-ahead schedule is created by identifying critical tasks for a given duration (2-3 weeks), then breaking each task into more granular sub-tasks while reviewing the resource allocation for accuracy. This detail-oriented focus helps to ensure long-term schedule adherence.
6. Use specialized construction scheduling software
Available software tools go beyond simple Gantt charts and templates to bring real-time analysis, error-proofing, and customizable formats to the table while supporting timely status reporting. Construction scheduling software allows project managers to create detailed and accurate schedules more easily with automated change and resource management features to ensure the schedule reflects the latest project conditions.
Advanced construction software solutions also allow schedules to be integrated with labor tracking and material databases to make time, cost, and resource dependencies more visible. RIB Candy is one of those tools, offering advanced estimating, planning, and project control capabilities, as well as intuitive critical path planning to support effective schedule building and resource allocation.
Conclusion
The construction scheduling process has come a long way since the first paper-based methods were devised to logically map out task durations and resources. These processes are now poised to enter a fully digital era, with Building Information Modeling (BIM), advanced algorithms, and cloud-based platforms automating and streamlining scheduling tasks so that project managers can focus on the issues that matter most.
RIB Candy supports this digital transformation with advanced planning and scheduling features integrated into a user-friendly platform. Customizable layouts, reports, and graphing methods dramatically improve the effectiveness of any construction schedule, ensuring unmatched levels of quality and profitability.
If you are ready to benefit from professional construction scheduling software and ensure your projects finish in the expected time and budget, get your free demo for RIB Candy today!
Most Recent
10 mins read
10 mins read
11 mins read
10 mins read
Blog Categories

Ebook











